Introduction
Cottage cheese has gained immense popularity in recent years, particularly among health-conscious individuals. Whether used as a snack, a breakfast option, or a protein-packed ingredient in meals, it offers a unique combination of taste and nutrition. But is it actually healthy to eat cottage cheese every day?
In this article, we will explore the nutritional value of cottage cheese, its health benefits, and potential risks associated with daily consumption. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of whether incorporating cottage cheese into your daily diet is a smart choice.
Nutritional Profile of Cottage Cheese
Cottage cheese is often considered a nutrient-dense food, making it a popular choice for individuals focused on maintaining a healthy diet. Let’s take a closer look at its macronutrient composition, essential vitamins, and how it compares to other dairy products.
Macronutrient Composition
Cottage cheese is primarily made up of three macronutrients: protein, fat, and carbohydrates. The exact composition varies depending on the fat content (full-fat, low-fat, or fat-free). Here’s an average breakdown per 100 grams of low-fat cottage cheese:
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 98 kcal |
| Protein | 11g |
| Fat | 4.3g |
| Carbohydrates | 3.4g |
| Calcium | 83mg |
| Sodium | 364mg |
- Protein: Cottage cheese is an excellent source of casein protein, which digests slowly, providing sustained amino acid release.
- Fat: The fat content varies significantly based on the type chosen (full-fat vs. fat-free).
- Carbohydrates: It has a relatively low carbohydrate content, making it a great option for low-carb and keto diets.
Vitamins and Minerals in Cottage Cheese
In addition to its macronutrients, cottage cheese contains essential vitamins and minerals that support various bodily functions:
- Calcium: Important for bone health and muscle function.
- Phosphorus: Works with calcium to strengthen bones and teeth.
- Vitamin B12: Essential for red blood cell formation and brain function.
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Helps in energy production and cell growth.
- Sodium: While necessary for electrolyte balance, its high levels in cottage cheese can be a concern for individuals with high blood pressure.
How Cottage Cheese Compares to Other Dairy Products
Compared to other dairy products, cottage cheese has a unique nutritional advantage:
| Dairy Product | Protein per 100g | Fat per 100g | Calories per 100g |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cottage Cheese | 11g | 4.3g | 98 kcal |
| Greek Yogurt | 10g | 3.8g | 97 kcal |
| Ricotta Cheese | 7g | 10g | 174 kcal |
| Cheddar Cheese | 25g | 33g | 402 kcal |
- Cottage cheese has higher protein content than ricotta but is lower in fat and calories than most cheeses.
- Unlike Greek yogurt, it has a chunkier texture but a similar protein profile.
 Health Benefits of Consuming Cottage Cheese Daily
Health Benefits of Consuming Cottage Cheese Daily
Eating cottage cheese daily can offer several health benefits, thanks to its rich nutrient profile. From aiding muscle growth to improving bone health, let’s explore the key advantages of incorporating this dairy product into your diet.
High Protein Content: Muscle Growth & Weight Management
One of the primary reasons people consume cottage cheese daily is its high protein content. With approximately 11g of protein per 100g, it serves as an excellent source of casein protein, which digests slowly, providing sustained amino acid release.
- Muscle Growth & Recovery – Casein protein is particularly beneficial for muscle repair and growth, making it a favorite among athletes and bodybuilders. Eating cottage cheese before bed provides a steady supply of amino acids overnight, aiding muscle recovery.
- Weight Management & Satiety – Protein-rich foods help you stay full longer, reducing cravings and unnecessary snacking. This makes cottage cheese a great option for weight loss and calorie control.
Rich in Calcium and Phosphorus: Bone Health Benefits
Calcium and phosphorus work together to strengthen bones and teeth. Cottage cheese contains 83mg of calcium per 100g, making it a beneficial food for:
- Preventing Osteoporosis – Regular intake helps maintain bone density, reducing the risk of fractures, especially in older adults.
- Supporting Dental Health – Calcium and phosphorus play a key role in tooth enamel strength and repair.
Contains B Vitamins: Energy & Brain Function
Cottage cheese is a natural source of B vitamins, including B12, B2 (riboflavin), and B6. These vitamins are essential for:
- Energy Production – B vitamins help convert food into energy, keeping you active throughout the day.
- Brain Health – Vitamin B12 is crucial for cognitive function and memory retention, reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Low in Calories: A Great Choice for Dieters
For those following a calorie-restricted diet, cottage cheese is an excellent choice.
- A 100g serving contains only 98 kcal, making it an ideal snack for those looking to lose weight.
- When combined with fruits, vegetables, or whole grains, it becomes a balanced meal that supports weight loss without compromising nutrition.
 Potential Risks and Considerations
Potential Risks and Considerations
While cottage cheese offers numerous health benefits, consuming it daily may not be suitable for everyone. There are some potential risks to consider, particularly regarding sodium content, lactose intolerance, and additives.
High Sodium Content: Impact on Blood Pressure
One major concern with cottage cheese is its high sodium content. A 100g serving contains 364mg of sodium, which can be problematic for:
- Individuals with Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) – Excess sodium intake is linked to increased blood pressure, which can raise the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- People with Kidney Issues – High sodium levels can put additional strain on the kidneys, potentially worsening kidney disease.
How to Reduce Sodium Intake from Cottage Cheese:
- Opt for low-sodium or unsalted varieties to minimize health risks.
- Rinse regular cottage cheese with water in a strainer to remove some sodium.
Lactose Content: Issues for Lactose-Intolerant Individuals
Cottage cheese contains lactose, a natural sugar found in dairy that some people have difficulty digesting. Those with lactose intolerance may experience:
- Bloating
- Gas
- Diarrhea
Alternatives for Lactose-Intolerant Individuals:
- Choose lactose-free cottage cheese, which is now widely available in stores.
- Opt for dairy-free alternatives like almond, soy, or cashew-based cheese substitutes.
Possible Additives: Added Sugars and Preservatives
Not all cottage cheese products are the same. Some flavored or processed varieties contain:
- Added sugars – Increases calorie count and may lead to weight gain.
- Preservatives – May cause digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals.
How to Choose a Healthier Cottage Cheese:
- Check the ingredient list – Opt for brands with minimal additives.
- Choose plain, organic, or homemade cottage cheese to ensure natural ingredients.
 Cottage Cheese in Weight Management
Cottage Cheese in Weight Management
Cottage cheese is often included in weight loss and weight management diets due to its high protein, low calorie, and filling properties. Whether you’re aiming to shed pounds or maintain a healthy weight, this dairy product can be an excellent addition to your daily diet.
How Cottage Cheese Supports Weight Loss
One of the biggest challenges in weight loss is controlling hunger and calorie intake. Cottage cheese helps in several ways:
- High in Protein, Low in Calories – A 100g serving contains about 98 kcal and 11g of protein, making it an efficient, nutrient-dense food for weight loss.
- Keeps You Fuller for Longer – The casein protein in cottage cheese digests slowly, keeping you satisfied for hours and reducing cravings.
- Boosts Metabolism – Protein has a high thermic effect, meaning your body burns more calories digesting it compared to fats or carbs.
Cottage Cheese in Different Diet Plans
- Cottage cheese is versatile and can fit into various dietary strategies:
| Diet Type | How Cottage Cheese Fits In |
|---|---|
| Low-Calorie Diets | Low in calories and high in protein, making it ideal for calorie control. |
| Ketogenic (Keto) Diet | Choose full-fat cottage cheese for a low-carb, high-fat option. |
| Intermittent Fasting (IF) | A great post-fasting meal due to its protein content and easy digestion. |
| High-Protein Diets | Supports muscle preservation and fat loss simultaneously. |
| Vegetarian Diets | A great meat alternative for vegetarians seeking protein sources. |
Best Ways to Eat Cottage Cheese for Weight Loss
- As a Snack: Enjoy it plain or mixed with cinnamon, nuts, or berries.
- As a Meal Addition: Add to salads, whole-grain toast, or omelets for a protein boost.
- Before Bed: Eating cottage cheese before sleep supports muscle recovery and prevents late-night cravings.
Cottage Cheese and Muscle Building
Cottage cheese is a favorite among athletes, bodybuilders, and fitness enthusiasts due to its high protein content and slow digestion rate. It provides essential amino acids that aid in muscle repair, growth, and recovery.
Casein Protein: The Key to Muscle Growth
Unlike whey protein, which is rapidly absorbed, cottage cheese contains casein protein, which:
- Digests slowly, providing a steady release of amino acids over several hours.
- Prevents muscle breakdown, especially overnight or during long periods without food.
- Enhances muscle recovery, making it ideal as a pre-bedtime meal.
Benefits for Athletes and Bodybuilders
For those who engage in resistance training, weightlifting, or endurance sports, cottage cheese offers:
- Sustained Protein Supply – Supports muscle protein synthesis for continuous muscle repair.
- Low-Carb, High-Protein Ratio – Helps maintain lean muscle mass while reducing body fat.
- Improved Strength & Performance – Essential nutrients like calcium and phosphorus support muscle contraction and energy production.
Best Times to Eat Cottage Cheese for Muscle Gains
| When to Eat | Why It’s Beneficial |
|---|---|
| Before Bed | Casein protein prevents overnight muscle breakdown and enhances recovery. |
| Post-Workout | Provides essential amino acids for muscle repair and growth. |
| Between Meals | A protein-rich snack that keeps you full and prevents muscle loss. |
How to Incorporate Cottage Cheese into a Muscle-Building Diet
- Smoothies & Shakes – Blend with banana, protein powder, and nut butter for a high-protein drink.
- Pre-Bedtime Snack – Eat plain or mixed with almonds and chia seeds for sustained protein release.
- Omelets & Scrambles – Add to eggs for an extra muscle-building protein boost.
 Impact on Bone Health
Impact on Bone Health
Cottage cheese is a bone-strengthening powerhouse, thanks to its rich calcium, phosphorus, and protein content. These nutrients play a crucial role in maintaining bone density, preventing fractures, and reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
How Cottage Cheese Supports Strong Bones
| Nutrient | Bone Health Benefit |
|---|---|
| Calcium | Strengthens bones, prevents fractures, and supports bone regeneration. |
| Phosphorus | Works with calcium to enhance bone mineral density. |
| Protein | Helps in bone growth, repair, and maintenance. |
| Vitamin B12 | Supports bone cell formation and reduces age-related bone loss. |
- Cottage cheese provides around 83mg of calcium per 100g, contributing to daily calcium needs for strong bones.
- Studies show that consuming high-protein dairy like cottage cheese helps reduce bone loss in aging adults.
Preventing Osteoporosis and Bone-Related Disorders
Regular consumption of calcium-rich foods like cottage cheese can:
- Reduce the risk of osteoporosis, a condition where bones become weak and brittle.
- Support bone regeneration and repair in athletes and active individuals.
- Improve bone density in women, particularly after menopause.
Best Ways to Eat Cottage Cheese for Bone Health
- Pair with Vitamin D-rich Foods – Eat with fortified cereals, eggs, or mushrooms for better calcium absorption.
- Combine with Nuts & Seeds – Almonds and sesame seeds provide additional bone-strengthening minerals.
- Include in Meals Regularly – Add to smoothies, toast, or salads to increase daily calcium intake.
Effects on Blood Sugar Levels
Cottage cheese is an excellent choice for people managing blood sugar levels, including those with diabetes. Thanks to its low carbohydrate content and high protein levels, it has minimal impact on blood sugar spikes.
Low Carbohydrate Content: Ideal for Blood Sugar Control
Unlike many dairy products that contain more lactose (milk sugar), cottage cheese is relatively low in carbohydrates.
| Dairy Product | Carbohydrates per 100g |
|---|---|
| Cottage Cheese | 3.4g |
| Greek Yogurt | 4g |
| Regular Yogurt | 10g |
| Milk | 12g |
- Since it contains only 3.4g of carbs per 100g, it does not cause rapid glucose spikes, making it ideal for diabetics and those on low-carb diets.
Suitable for Diabetics and Pre-Diabetics
Cottage cheese has a low glycemic index (GI), meaning it releases glucose into the bloodstream slowly. This helps:
- Stabilize blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Reduce the risk of insulin resistance, a key factor in type 2 diabetes.
- Support weight loss, which is essential for blood sugar management.
How Cottage Cheese Compares to Other Dairy in Glycemic Control
| Dairy Product | Glycemic Index (GI) | Blood Sugar Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cottage Cheese | Low (30-35) | Minimal |
| Greek Yogurt | Low (35-40) | Minimal |
| Regular Yogurt | Moderate (50-60) | Moderate |
| Milk | Moderate (40-45) | Moderate |
- Choosing plain, unsweetened cottage cheese is best for blood sugar control.
- Flavored or fruit-added versions may contain added sugars, which can spike glucose levels.
Best Ways to Eat Cottage Cheese for Blood Sugar Balance
- Pair with Fiber-Rich Foods – Add berries, flaxseeds, or nuts to slow digestion.
- Avoid Added Sugar Varieties – Stick to plain or organic options.
- Combine with Healthy Fats – Eating cottage cheese with avocado, olive oil, or nuts enhances blood sugar stability.
 Gut Health and Probiotics
Gut Health and Probiotics
Gut health plays a crucial role in digestion, immunity, and overall well-being, and cottage cheese can be a beneficial food for supporting a healthy gut microbiome—especially when it contains live probiotics.
Does Cottage Cheese Contain Probiotics?
Not all cottage cheese contains live probiotic cultures, but some brands do. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that help:
- Improve digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Support immune function by promoting good gut bacteria.
- Reduce symptoms of bloating, gas, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Benefits of Probiotic-Rich Cottage Cheese
| Benefit | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Improves Digestion | Supports healthy bowel movements and reduces bloating. |
| Enhances Immunity | A balanced gut microbiome strengthens immune defenses. |
| Supports Mental Health | Gut health is linked to reduced stress and better mood. |
| Prevents Infections | Helps combat harmful bacteria and yeast overgrowth. |
How to Choose Probiotic Cottage Cheese
If you want the gut health benefits, look for cottage cheese with live cultures.
Check the Label for:
- Phrases like “contains live and active cultures.”
- Probiotic strains such as Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium.
- Minimal additives and preservatives (which can affect gut health).
Alternatives for Gut Health if Cottage Cheese Lacks Probiotics
If your favorite cottage cheese doesn’t contain probiotics, consider adding other fermented foods like:
- Greek yogurt
- Kefir
- Sauerkraut or kimchi
- Kombucha
Best Ways to Eat Cottage Cheese for Gut Health
- With Fiber-Rich Foods – Combine with fruits like bananas, apples, or chia seeds for improved digestion.
- With Fermented Foods – Mix into a meal containing yogurt or pickled vegetables for a gut-friendly dish.
- As a Topping for Whole Grains – Use on whole grain toast or oats to promote a balanced microbiome.
 Versatility in Culinary Uses
Versatility in Culinary Uses
One of the best things about cottage cheese is its versatility in the kitchen. It can be used in sweet or savory dishes, making it a convenient and nutritious addition to almost any meal.
How to Incorporate Cottage Cheese into Everyday Meals
| Meal Type | Ways to Use Cottage Cheese |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Mixed with berries, honey, and nuts or spread on whole-grain toast. |
| Lunch | Added to salads, sandwiches, or wraps for extra protein. |
| Dinner | Used in pasta dishes, casseroles, or soups. |
| Snacks | Eaten plain, with crackers, veggies, or nut butter. |
| Desserts | Blended into smoothies, cheesecakes, or pancakes. |
Sweet vs. Savory Applications
Sweet Options:
- Mix with fruit and cinnamon for a healthy, high-protein dessert.
- Blend with banana and cocoa powder for a creamy, chocolatey snack.
- Add to oatmeal for an extra boost of protein.
Savory Options:
- Use as a base for dips with herbs and spices.
- Add to scrambled eggs for a creamy texture.
- Stir into mashed potatoes for a protein-rich alternative to butter.
Easy Cottage Cheese Recipes
 Creamy Cottage Cheese & Honey Toast
Creamy Cottage Cheese & Honey Toast
Ingredients
- 2 slices of whole-grain bread
- ½ cup cottage cheese
- 1 tbsp honey
- 1 tbsp chopped almonds or walnuts
- Fresh berries (strawberries, blueberries, or raspberries)
- A pinch of cinnamon (optional)
Directions
- Toast the bread until golden brown and crispy.
- Spread a generous layer of cottage cheese on each slice.
- Drizzle honey over the top for natural sweetness.
- Sprinkle with chopped nuts and fresh berries.
- Finish with a pinch of cinnamon for extra flavor. Serve immediately and enjoy!
 Cottage Cheese Avocado Toast
Cottage Cheese Avocado Toast
Ingredients
- 2 slices of whole-grain or sourdough bread
- 1 ripe avocado, mashed
- ½ cup cottage cheese
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- Salt & pepper to taste
- A pinch of red pepper flakes (optional)
- 1 tbsp fresh chives or cilantro, chopped (optional)
- 3-4 cherry tomatoes, sliced (optional)
- 1 poached or fried egg (optional, for extra protein)
Directions
- Toast the bread until golden brown and crispy.
- In a bowl, mash the avocado with lemon juice, salt, and pepper.
- Spread a layer of cottage cheese on the toast.
- Top with mashed avocado, then sprinkle with red pepper flakes and fresh herbs.
- Add sliced cherry tomatoes or a poached egg for extra flavor. Serve immediately and enjoy!
 Savory Cottage Cheese Dip
Savory Cottage Cheese Dip
Ingredients
- 1 cup cottage cheese
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 small garlic clove, minced
- 1 tbsp fresh chives, finely chopped
- 1 tbsp fresh parsley, chopped
- 1 tbsp olive oil
- ½ tsp salt
- ¼ tsp black pepper or red pepper flakes (optional)
- Fresh veggies (carrots, cucumbers, bell peppers) for dipping
Directions
- In a food processor or blender, blend cottage cheese, lemon juice, garlic, olive oil, salt, and pepper until smooth.
- Stir in chopped chives and parsley.
- Transfer to a bowl and drizzle with a little more olive oil.
- Serve with fresh veggies, crackers, or pita chips.
- Enjoy as a healthy snack, appetizer, or spread!
Can Cottage Cheese Be Used in Cooking and Baking?
Yes! Cottage cheese can be used in baked goods and cooked dishes:
- As a ricotta substitute in lasagna or stuffed pasta.
- In pancakes or muffins to increase protein.
- As a creamy base for soups or sauces.
Considerations for Specific Populations
Cottage cheese can be a great addition to many diets, but certain groups of people should pay special attention to how and when they consume it. Below, we explore how pregnant women, the elderly, and children can benefit from or need to be cautious about eating cottage cheese daily.
Pregnant Women: Is Cottage Cheese Safe?
Cottage cheese is generally safe for pregnant women, but they should be careful about:
- Unpasteurized Cottage Cheese – Some raw dairy products may contain Listeria, a bacteria that can be harmful to both the mother and baby. Always choose pasteurized varieties.
- High Sodium Levels – Excess sodium can contribute to water retention and high blood pressure during pregnancy.
- Protein and Calcium Benefits – Cottage cheese provides essential nutrients for fetal development, including protein, calcium, and B vitamins.
Best Ways for Pregnant Women to Eat Cottage Cheese:
- Mixed with fruit and nuts for a balanced snack.
- Combined with vegetables and whole grains for a nutrient-packed meal.
Elderly Individuals: Bone Health and Muscle Preservation
Aging comes with an increased risk of osteoporosis and muscle loss (sarcopenia), making cottage cheese a great dietary choice for older adults.
Benefits for Seniors:
- Supports Bone Strength – High calcium and phosphorus content prevents bone loss.
- Maintains Muscle Mass – The slow-digesting casein protein helps reduce muscle breakdown.
- Easy to Digest – Soft texture and mild flavor make it suitable for those with chewing difficulties.
Best Ways for Elderly Individuals to Eat Cottage Cheese:
- Blended into soups or smoothies for easy consumption.
- Paired with soft fruits or oatmeal for a gentle, nutritious meal.
Children and Adolescents: Growth and Development
Children and teens need high-protein, nutrient-dense foods for proper growth, and cottage cheese is an excellent source of essential vitamins and minerals.
Why Cottage Cheese is Great for Kids:
- Rich in Protein – Supports muscle development and brain function.
- Provides Essential Calcium – Helps build strong bones and teeth.
- A Healthy Alternative to Sugary Snacks – Can be used in smoothies, sandwiches, or pancakes.
Considerations for Kids:
- Some children may dislike the texture of cottage cheese. Mixing it with other foods like yogurt or fruit can help.
- Always choose low-sodium, unsweetened options to avoid unnecessary additives.
Best Ways for Children to Eat Cottage Cheese:
- Mixed with fruit and honey as a snack.
- Blended into smoothies for a creamy texture.
- Added to scrambled eggs or pasta dishes for extra protein.
 Comparing Cottage Cheese with Other Dairy Products
Comparing Cottage Cheese with Other Dairy Products
Cottage cheese is often compared to yogurt, ricotta, and other cheeses, but how does it truly stack up in terms of nutrition, texture, and dietary benefits? Let’s break it down.
12.1 Nutritional Differences Between Cottage Cheese and Other Dairy Products
| Dairy Product | Calories (per 100g) | Protein (g) | Fat (g) | Carbs (g) | Calcium (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cottage Cheese | 98 kcal | 11g | 4.3g | 3.4g | 83mg |
| Greek Yogurt | 97 kcal | 10g | 3.8g | 4g | 110mg |
| Ricotta Cheese | 174 kcal | 7g | 10g | 3g | 207mg |
| Cheddar Cheese | 402 kcal | 25g | 33g | 1.3g | 721mg |
Key Takeaways:
- Cottage cheese has fewer calories than ricotta and cheddar.
- Higher in protein than ricotta, making it a better choice for muscle building and weight loss.
- Lower in calcium than cheddar or Greek yogurt but still a good source.
- Lower in fat than aged cheeses like cheddar.
Texture and Taste Differences
| Dairy Product | Texture | Taste |
|---|---|---|
| Cottage Cheese | Soft, lumpy | Mild, slightly tangy |
| Greek Yogurt | Thick, creamy | Tart, tangy |
| Ricotta Cheese | Smooth, grainy | Sweet, mild |
| Cheddar Cheese | Firm, crumbly | Sharp, rich |
Who Should Choose Cottage Cheese?
- People looking for a high-protein, low-calorie option.
- Those who enjoy a mild, neutral taste (easier to mix with sweet or savory foods).
- Anyone wanting a versatile dairy product for both cooking and snacking.
Who Might Prefer Other Dairy Products?
- Greek Yogurt – Better for probiotic benefits and gut health.
- Ricotta Cheese – Great for desserts and creamy dishes.
- Cheddar Cheese – Ideal for those needing higher calcium and fat intake.
How to Choose the Right Cottage Cheese
Not all cottage cheese is created equal! With so many varieties available, it’s important to know what to look for on the label to ensure you’re getting the healthiest option.
Understanding Labels: Fat Content, Sodium, and Live Cultures
When buying cottage cheese, check for these key factors:
Fat Content:
- Full-Fat (4%) – Richer taste, creamier texture, and higher in calories.
- Low-Fat (1-2%) – Balanced option for protein and calorie control.
- Fat-Free (0%) – Lowest in calories but can taste dry or grainy.
Sodium Levels:
- Standard cottage cheese contains 300-400mg of sodium per 100g.
- Low-sodium options (100-200mg sodium) are better for heart health.
- To reduce sodium, rinse cottage cheese under water before eating.
Live and Active Cultures:
- Some brands add probiotics for gut health benefits.
- Look for labels stating “contains live and active cultures.”
Tips for Selecting Quality Products
What to Look For:
- Simple ingredients: Avoid added sugars, gums, and preservatives.
- Organic or grass-fed options: Higher in omega-3s and better fat quality.
- No artificial flavors: Stick to plain cottage cheese and add your own fruit or spices.
What to Avoid:
- Flavored varieties (often high in sugar and artificial additives).
- Cottage cheese with thickeners (guar gum, carrageenan, modified starches).
- Ultra-processed brands with excessive preservatives.
Storage and Shelf-Life Considerations
- Refrigerate cottage cheese at all times.
- Consume within 5-7 days after opening.
- If it smells sour or has mold, discard immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some of the most common questions people ask about eating cottage cheese daily.
How much cottage cheese is recommended daily?
The ideal amount depends on your nutritional needs:
- For general health – ½ to 1 cup per day provides sufficient protein and nutrients.
- For muscle building – 1 to 1.5 cups per day can support protein intake.
- For weight loss – ½ to 1 cup per day, paired with fiber-rich foods, helps with satiety.
Can lactose-intolerant individuals eat cottage cheese?
It depends on individual tolerance levels.
- Cottage cheese contains less lactose than milk but may still cause discomfort.
- Lactose-free cottage cheese is available for those with sensitivity.
Is cottage cheese suitable for vegans?
No. Cottage cheese is a dairy-based product.
- Vegan alternatives include almond, cashew, or soy-based cheeses.
Does cottage cheese contribute to weight gain?
Not necessarily.
- Low-fat cottage cheese is low in calories and helps with weight loss.
- Full-fat cottage cheese has more calories and fat but can be part of a balanced diet if eaten in moderation.
What are some easy recipes using cottage cheese?
Cottage cheese can be used in both sweet and savory dishes:
- Breakfast: Mix with fruit, honey, and nuts.
- Lunch/Dinner: Add to salads, eggs, or whole-grain toast.
- Snacks: Blend into smoothies or use as a dip for veggies.
How does cottage cheese compare to Greek yogurt in terms of protein?
Both are high-protein dairy options, but:
- Cottage cheese has slightly more protein per serving (11g vs. 10g per 100g).
- Greek yogurt has probiotics, making it a better option for gut health.
- Cottage cheese is lower in carbs, making it preferable for low-carb diets.
Conclusion
Cottage cheese is a nutrient-dense, high-protein dairy product that can be a healthy daily addition to most diets. It provides essential nutrients like calcium, protein, and B vitamins, supporting muscle growth, weight management, and bone health.
However, it’s important to consider individual dietary needs:
- Choose low-sodium varieties if you have high blood pressure.
- Opt for lactose-free options if you’re sensitive to dairy.
- Pick plain, additive-free brands for maximum health benefits.
When consumed in moderation, cottage cheese is a versatile, nutritious food that can benefit athletes, weight-conscious individuals, and people of all ages.
More Delicious Recipes
Colombian Breakfast Recipes: 15 Authentic Dishes to Try at Home!
Can You Make Flatbread with Cottage Cheese? A High-Protein Recipe & Guide
Cottage Cheese Avocado Toast: A Protein-Packed, Healthy & Delicious Recipe

 Health Benefits of Consuming Cottage Cheese Daily
Health Benefits of Consuming Cottage Cheese Daily Potential Risks and Considerations
Potential Risks and Considerations Cottage Cheese in Weight Management
Cottage Cheese in Weight Management Impact on Bone Health
Impact on Bone Health Gut Health and Probiotics
Gut Health and Probiotics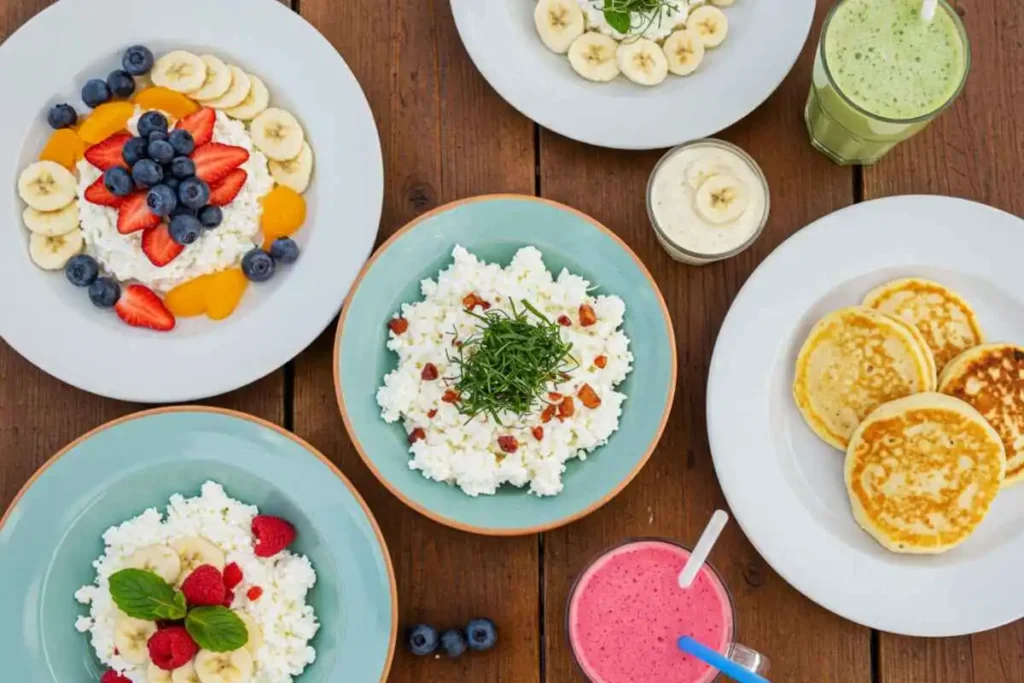 Versatility in Culinary Uses
Versatility in Culinary Uses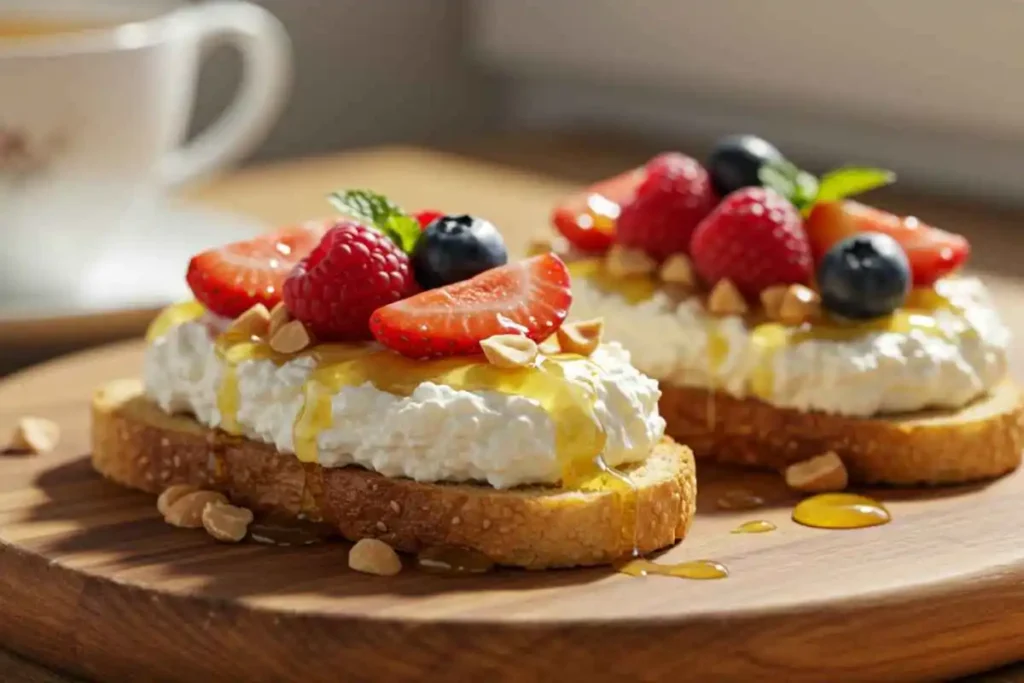 Creamy Cottage Cheese & Honey Toast
Creamy Cottage Cheese & Honey Toast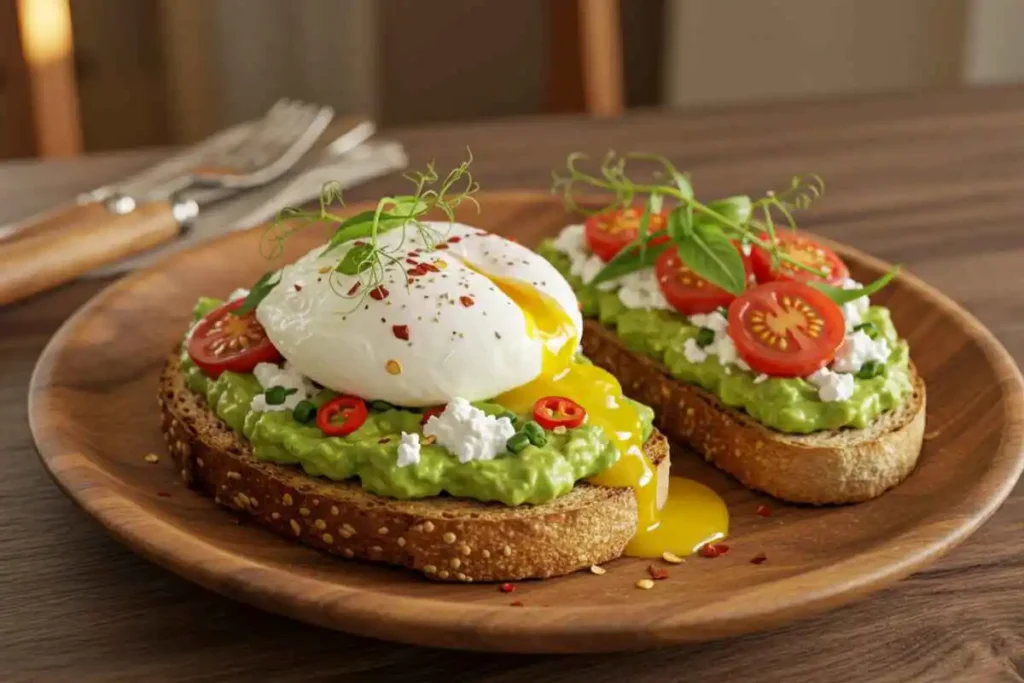 Cottage Cheese Avocado Toast
Cottage Cheese Avocado Toast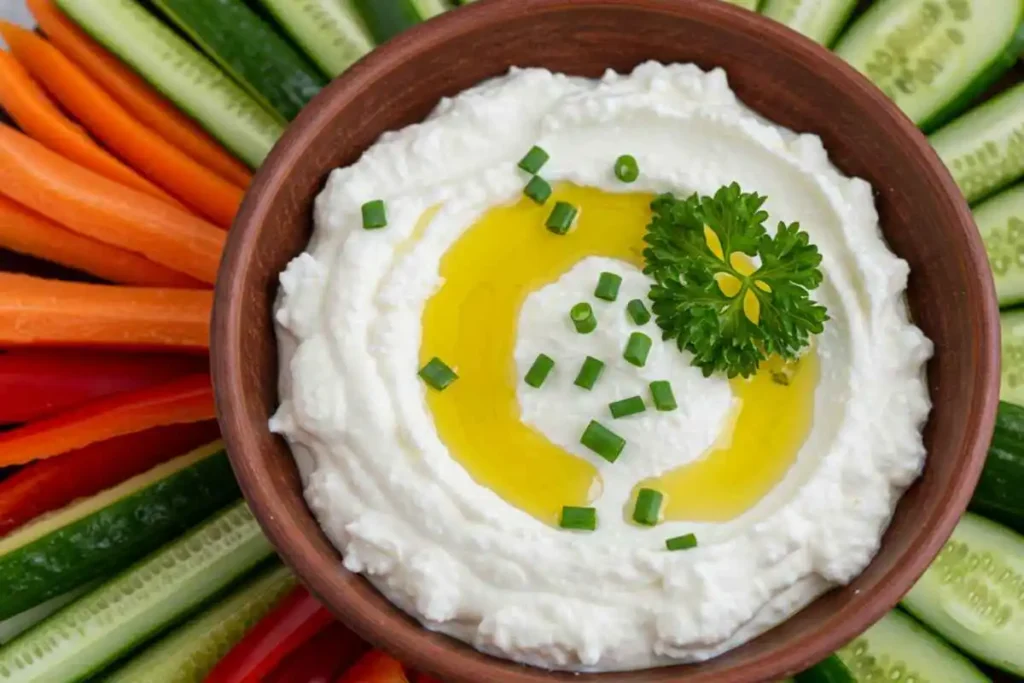 Savory Cottage Cheese Dip
Savory Cottage Cheese Dip Comparing Cottage Cheese with Other Dairy Products
Comparing Cottage Cheese with Other Dairy Products